Billions of dollars are lost each year because weld decisions are made by individuals who do not understand weld process fundamentals. With the proper training, your organization will no longer be guessing when it comes to welding. Your staff will have all the tools needed to make informed welding decisions and boost company profits.
Advanced Welding Solutions offers customized training programs to help educate your employees in basic and advanced topics related to welding and brazing. All training programs are specifically designed for your organization and target audience. Providing training for employees on topics that are relevant to their job function provides an instant return on investment.
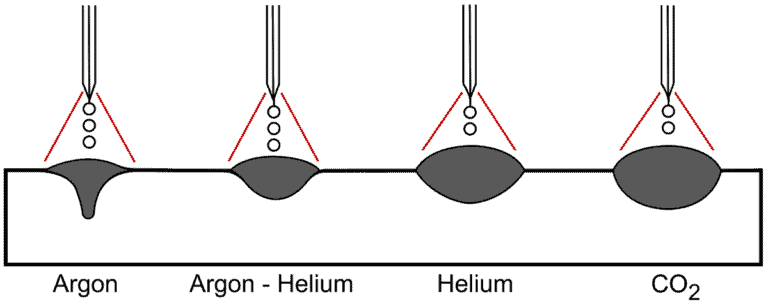
• Gas metal arc welding (GMAW) — aka MIG
• Flux cored arc welding (FCAW)
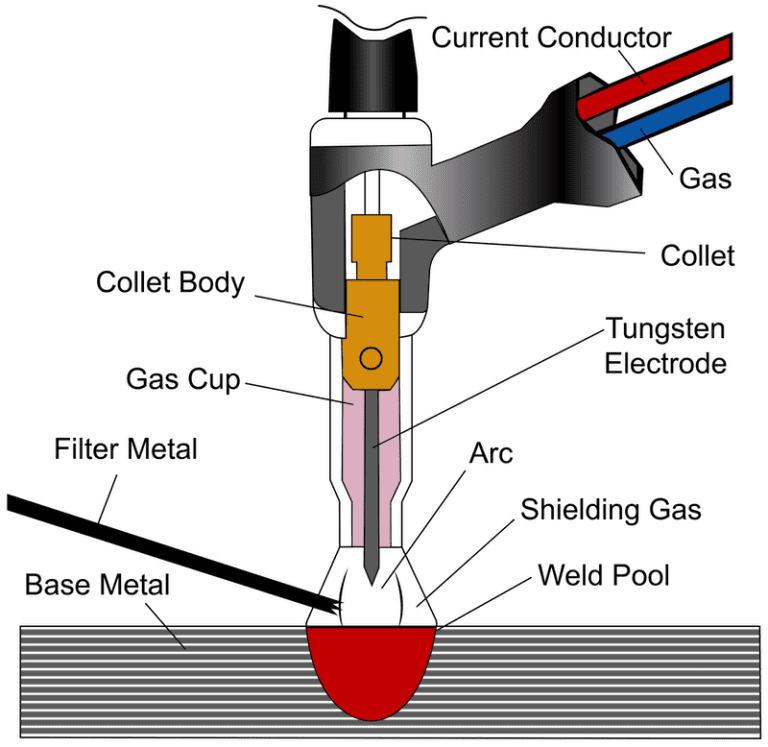
• Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) — aka TIG
• Plasma arc welding (PAW)
• Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) — aka stick
• Submerged arc welding (SAW)
• Laser beam welding (LBW)
• Electron beam welding (EBW)
• Resistance spot welding (RSW)
• Projection welding (PW)
• Brazing (torch, furnace, induction, etc.)
• …many more!

Engineers are often the decision makers when it comes to welding specifications, joint design, and joint selection. These details are often communicated to the fabrication staff via technical drawings which include welding symbols. It is expected that the engineer properly uses the correct welding symbol and that welders and inspectors correctly interpret and apply them.
Advanced Welding Solutions helps your welding team “crack the code” with a course that covers:
• Weld joint geometry
• Welding symbols
• Technical drawing use and interpretation

It is crucial for companies performing welding to code requirements to have engineers, quality staff, and inspectors competent in code usage. Advanced Welding Solutions can train your staff in navigating these confusing and difficult to understand documents. We provide training for codes and standards developed by the following organizations:
• American Welding Society (AWS)
• American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME)
• Naval Sea Systems Command (NAVSEA)
• National Board of Boiler and Pressure Vessel Inspectors (NBBPVI)
• American Petroleum Institute (API)
• …and many more!
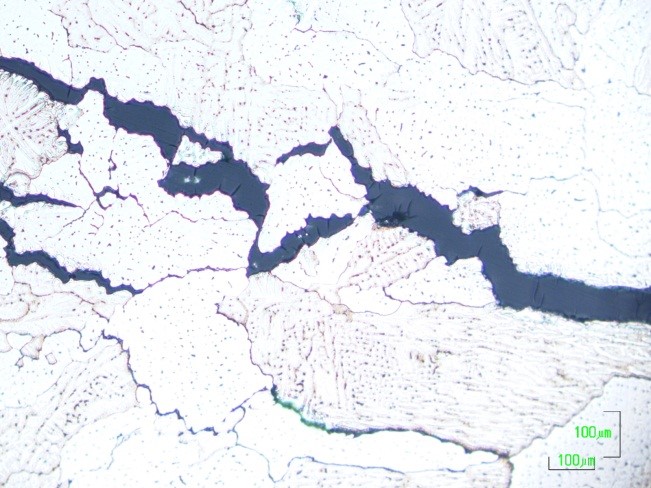

Welding metallurgy plays a crucial role in manufacturing processes. Understanding the behavior of metals during welding is essential for ensuring the structural integrity and performance of welded components. By studying the interaction between heat, filler material, and base metals, manufacturers can optimize welding techniques to achieve cost-effective, strong, and reliable welds. Advanced Welding Solutions will tailor training to your specific organizational needs in the following material science topics:
• Welding of carbon steels, low-alloy steels, stainless steels, cast irons, aluminum alloys, nickel alloys, copper alloys, magnesium alloys, titanium alloys and dissimilar metal joining
• Heat treatment (annealing, normalizing, stress relieving, tempering, etc.)
Weldment properties are determined by the material’s microstructure which is affected by its chemical composition and thermal cycle. Depending on the welding process and parameters used during welding (filler material, current, voltage, travel speed, shielding gas, etc.), the properties of the weld and heat-affected zone can vary dramatically. Common properties your staff should be aware of include:
• Tensile strength
• Ductility
• Hardness
• Toughness
• Fatigue strength
• Corrosion resistance
• Electrical resistivity
• Magnetism
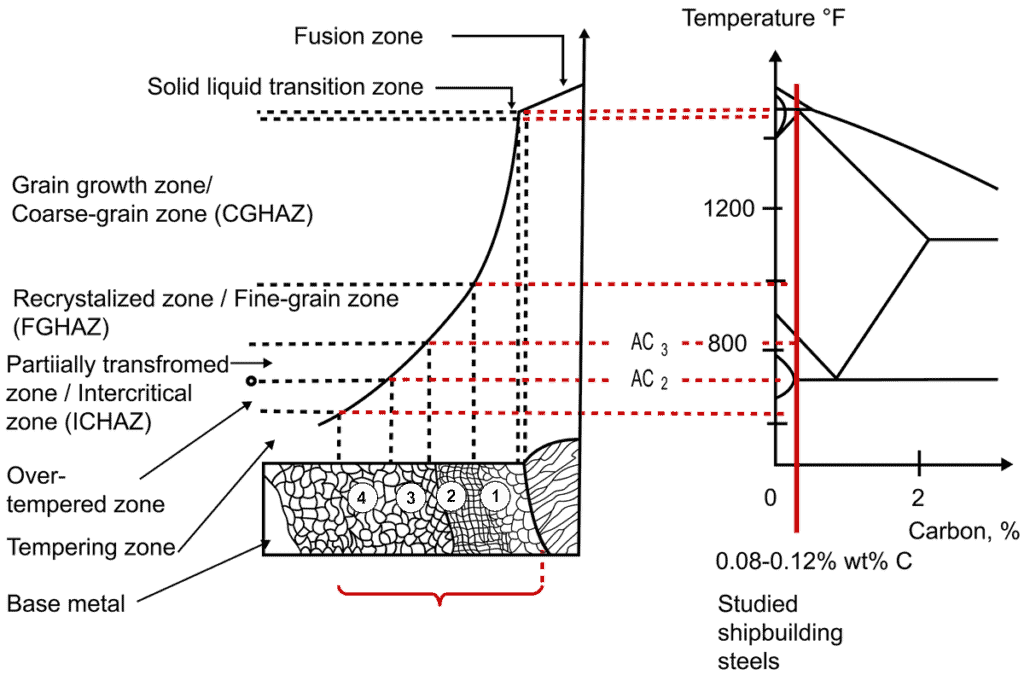
It is important the engineers and welding staff develop welding procedures that consider the metallurgical changes that occur during welding. To ensure the quality of finished work, your company’s staff should be competent in weld testing methods that determine weld quality. A few common destructive testing methods include:
• Tensile testing
• Fatigue testing
• Bend testing
• Nick break
• Fillet-weld break
• Macro examination
• Toughness (Charpy v-notch) testing
• Hardness testing

Any weld professional should be able to correctly identify weld defects and their causes. All too often organizations adjust machine settings until they get the desired result by arbitrarily adjusting machine controls. Save time, money, and frustration with our course about how to identify defects and then make the correct process adjustments to remedy the situation. Our course covers welding defects, base metal discontinuities, and process fundamentals relating to:
• Cracks
• Incomplete fusion
• Slag inclusion
• Tungsten inclusion
• Porosity
• Undercut
• Convexity/concavity
• Underfill
• Overlap
• Weld reinforcement
• Arc strike
• Spatter
• Lamination
• Lamellar tear
• Seam/lap
• Dimensional/distortion
• Incomplete joint penetration
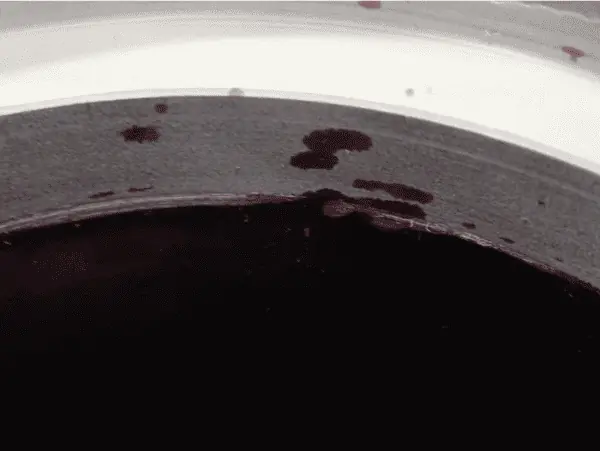
The first and most important visual inspector is the welder or a weld operator trained in various discontinuities. These employees get the first look at the finished weld and final say before the component is sent to the next operation.
Advanced Welding Solutions will train your staff on the use of weld inspection methods and how to determine compliance with acceptance criteria. We will also teach your staff about the various NDE techniques, their capabilities and limitations. Common NDE techniques we cover include:
• Visual testing (VT)
• Penetrant testing (PT)
• Magnetic particle testing (MT)
• Radiographic testing (RT)
• Ultrasonic testing (UT)
• Eddy current testing (ET)

Safety is an important consideration for any welding department. To help ensure the safety of the employees at your facility – make sure your team has thorough training in the potential safety hazards related to welding:
• Electric shock
• Falling
• Radiation
• Eye hazards (UV & debris)
• Smoke and fumes
• Falling objects

Based in Cleveland, Ohio
Fusing ideas with reality.